- IRS forms
- Form 8038-B
Form 8038-B: Information Return for Build America Bonds and Recovery Zone Economic Development Bonds
Download Form 8038-BIn the world of finance and taxation, there are numerous forms and regulations that can be overwhelming for both individuals and businesses. One such form is the IRS Form 8038-B, which pertains to Build America Bonds (BABs) and Recovery Zone Economic Development Bonds (RZEDBs).
These bonds have played a significant role in stimulating economic growth and development in the United States, and understanding the reporting requirements is crucial for bond issuers and investors alike.
In this blog, we will explore Form 8038-B in detail.
Understanding Form 8038-B
Form 8038-B is an "Information Return for Build America Bonds and Recovery Zone Economic Development Bonds" that must be filed by issuers of BABs and RZEDBs with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The purpose of this form is to report essential information related to these bonds and to ensure compliance with the tax requirements associated with their issuance.
Before diving into Form 8038-B, let's briefly touch on what Build America Bonds and Recovery Zone Economic Development Bonds are.
Build America Bonds (BABs): BABs are taxable municipal bonds that were introduced as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009. Unlike traditional tax exempt municipal bonds, BABs pay taxable interest to investors. To incentivize the issuance of these bonds, the U.S. Treasury Department provides a direct subsidy payment to the bond issuer, covering a percentage of the interest paid to investors.
Recovery Zone Economic Development Bonds (RZEDBs): RZEDBs were also established under the same legislation to help stimulate economic development in designated recovery zones. These bonds are tax exempt municipal bonds, meaning the interest paid to investors is generally not subject to federal income tax.
Purpose of Form 8038-B
The purpose of Form 8038-B is to provide information about the bond issuance to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Here are the key points related to Form 8038-B:
**Tax exempt bonds: **Form 8038-B is specific to tax exempt bonds issued by state and local governments or other qualified issuers. These bonds are typically used to finance public infrastructure projects such as schools, hospitals, highways, and other essential facilities.
**Information reporting: **The form serves as an information return that provides details about the bond issuance, including the issuer's information, the purpose of the bond, the amount issued, the issue date, the maturity date, and any applicable private business use or payments.
IRS monitoring and compliance: By requiring issuers to file Form 8038-B, the IRS can monitor the issuance and use of tax exempt bonds to ensure compliance with relevant tax laws and regulations.
**Record-keeping: **Issuers must keep copies of the filed Form 8038-B and related records for their records. These records may be subject to review or audit by the IRS.
Benefits of Form 8038-B:
Form 8038-B is used primarily for compliance purposes and provides valuable information to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regarding these bonds. The benefits of Form 8038-B include:
**1. Compliance with IRS regulations: **Form 8038-B helps governmental issuers of tax exempt bonds to comply with IRS regulations. Filing the form ensures that issuers provide all the necessary information required by the IRS to monitor tax exempt bond transactions.
2. Tax exempt status confirmation: Filing Form 8038-B allows the issuer to confirm the tax exempt status of the bonds. This is crucial because tax exempt bonds provide certain tax advantages to bondholders, so it's important to maintain compliance to preserve their tax exempt status.
**3. Transparency and accountability: **By providing detailed information about the bond issue, Form 8038-B enhances transparency and accountability in the bond issuance process. It allows the IRS and other stakeholders to review the financial aspects of the bond issue and ensures that the funds are being used for qualified tax exempt purposes.
4. Comprehensive information: The form requires various details about the bond issuance, such as the issuer's information, the purpose of the bonds, the principal amount, the interest rate, and the repayment schedule. This comprehensive information aids the IRS in evaluating the impact of the bond issuance on the tax exempt bond market.
5. Monitoring tax compliance: Form 8038-B helps the IRS monitor whether the issuer is adhering to the tax rules associated with tax exempt bonds. This includes ensuring that the bond proceeds are used for eligible projects, such as infrastructure or public welfare initiatives.
6. Preventing fraud and abuse: By requiring detailed information, the form acts as a deterrent against potential fraud or abuse related to tax exempt bonds. The IRS can use the provided data to detect any irregularities or misuse of funds.
7. Maintaining market integrity: The availability of accurate information through Form 8038-B contributes to maintaining the integrity of the tax exempt bond market. Investors and stakeholders can make informed decisions based on the information disclosed by the issuer.
Who Is Eligible To File Form 8038-B?
The following entities are typically eligible to file Form 8038-B:
State and local governments: This includes states, cities, counties, and other political subdivisions of states.
**Governmental organizations: **Certain governmental entities or organizations that are created by state or local governments and have specific powers granted by those governments may also be eligible.
**Qualified 501(c)(3) organizations: **Certain non profit organizations that are tax exempt under section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code and meet other requirements can issue tax exempt bonds. These bonds are often referred to as "qualified 501(c)(3) bonds."
**Qualified small issue bonds: **These are bonds issued by small governments or qualified 501(c)(3) organizations for specific purposes, such as financing manufacturing facilities or providing student loans.
How To Complete Form 8038-B: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here's a general step-by-step guide to completing Form 8038-B:
Step 1: Obtain the form and instructions
Visit the official IRS website and search for "Form 8038-B." Download the form and the corresponding instructions.
Step 2: Gather required information
Before filling out the form, gather all the necessary information, which may include:
- General information about the issuer (government entity) of the bonds
- Details about the bonds, such as the issue date, maturity date, and face value
- The purpose of the bond issuance (e.g., financing a public project)
- Any prior bond issues related to the current one
- Information about the bond counsel and underwriter, if applicable
Step 3: Start filling out the form
Begin by entering the requested general information, such as the name of the issuer, address, Employer Identification Number (EIN), etc.
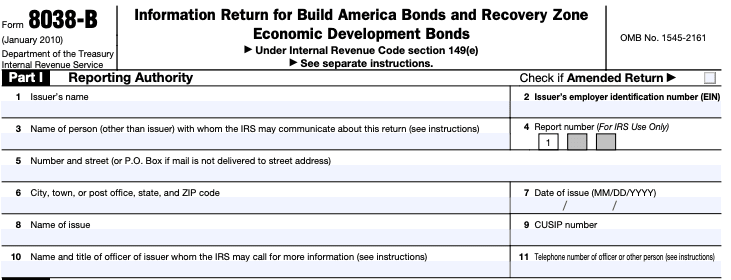
Step 4: Complete Part I
Part I gathers information about the issuer and the bond issue. This includes the purpose of the bond issue, the type of bonds being issued, and whether it's a new issue or a refunding.
Step 5: Complete Part II
Part II requires detailed information about the bond issue, such as the date of issue, maturity date, and the maximum face amount of bonds that may be issued.
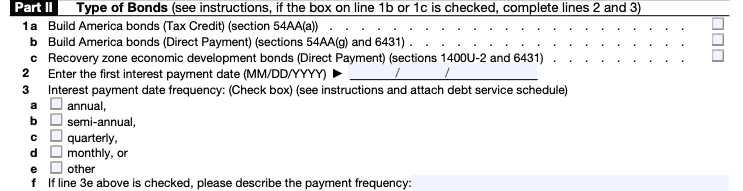
Step 6: Complete Part III
Part III deals with the use and certification of the issue. It requires information about the facilities or projects financed by the bond proceeds.

Step 7: Complete Part IV
Part IV relates to the arbitrage and rebate requirements, which ensure that tax exempt bonds are not used to generate excessive (link: https://fincent.com/glossary/profit text: profits). If applicable, provide information about compliance with these requirements.

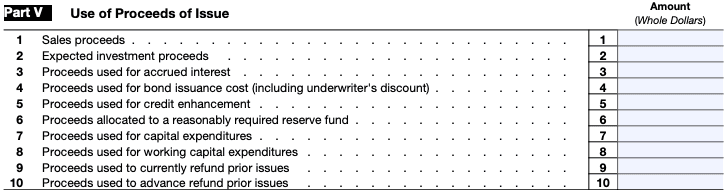
Step 8: Complete Part V
Part V is for issues of qualified mortgage bonds. If your bonds fall into this category, provide the necessary details as per the instructions.
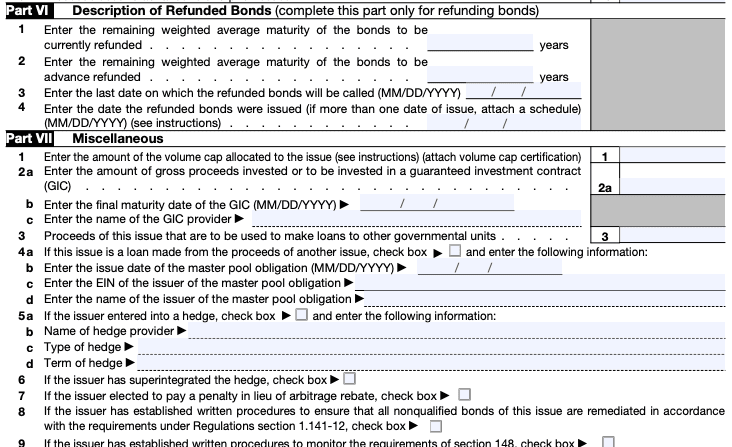
Step 9: Attach required documentation
Certain schedules, statements, or other documents might be required depending on the nature of the bond issue. Review the instructions carefully and attach any necessary supporting documentation.
Step 10: Sign and date the form
The issuer or an authorized official must sign and date the form.
Step 11: Retain a copy for your records
Before submitting the form to the IRS, make a copy of the completed form and all supporting documentation for your records.
Step 12: Submit the form
Mail the completed Form 8038-B and any required attachments to the address provided in the instructions.
Remember, Form 8038-B can be complex, and errors could lead to delays or other issues. If you are unsure about any part of the form or your specific bond issuance, seek advice from a qualified tax professional or consult the IRS for assistance.
Special Considerations When Filing Form 8038-B
When filing Form 8038-B, there are several special considerations that issuers should keep in mind to ensure compliance with IRS regulations. Here are some important considerations:
Accurate and timely filing: Ensure that Form 8038-B is filed accurately and on time. The form must be filed with the IRS no later than the 15th day of the 2nd month following the bond issue date.
Supporting documentation: Include all necessary supporting documentation, schedules, and attachments as required by the form's instructions. This may include copies of legal documents related to the bond issuance and any other relevant financial information.
Compliance with tax exempt bond rules: Ensure that the bond issuance complies with all relevant tax exempt bond rules and regulations. Failure to meet these requirements could result in the loss of tax exempt status for the bonds, leading to adverse tax consequences for bondholders and the issuer.
Proper identification: Provide accurate and complete identification information for both the issuer and the bond issue. This includes names, addresses, and taxpayer identification numbers (TINs) of all relevant parties.
**Private business use test: **Be aware of the private business use test, which limits the amount of private business use of the bond-financed facilities. If the test is not met, the bonds could be subject to taxation.
Arbitrage restrictions: Understand and comply with arbitrage restrictions, which limit the investment earnings on the bond proceeds to certain thresholds. Non-compliance with these rules may result in the loss of tax exempt status for the bonds.
Continuing disclosure requirements: In some cases, issuers are required to make ongoing disclosures to the Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board (MSRB) under the Securities and Exchange Commission's Rule 15c2-12. Ensure compliance with any applicable continuing disclosure requirements.
Record-keeping: Maintain adequate records and documentation related to the bond issuance for the required retention period. The IRS may request these records for examination purposes.
**Seek professional advice: **Given the complexity of tax exempt bond regulations, it's advisable for issuers to seek advice from qualified legal and financial professionals experienced in municipal bonds and tax law.
How To File 8038-B: Offline/Online/E-filing
Here's a general overview of the filing methods:
Offline filing
To file Form 8038-B offline, you would need to obtain a physical copy of the form from the IRS. You can order the form by calling the IRS at their toll-free number or by visiting your local IRS office. Once you have the form, fill it out manually with the necessary information and submit it by mail to the appropriate IRS address.
Online filing (IRS e-file)
The IRS offers an electronic filing option called IRS e-File. It allows tax exempt organizations to submit various forms electronically, including Form 8038-B. To use this method, you need to go to the official IRS website (www.irs.gov) and use their online submission system. You'll need to create an account and follow the instructions to complete and submit the form electronically.
E-filing through authorized providers
Instead of directly using the IRS e-File system, you can also use authorized third-party service providers to file Form 8038-B electronically. These providers offer software or online platforms that help with the preparation and submission of tax forms. Make sure to choose an IRS-authorized provider to ensure the security and accuracy of your submission.
IRS FIRE system (filing information returns electronically)
If you are an issuer or agent who needs to file many information returns, you can use the IRS FIRE system. This system is designed for bulk e-filing and requires the submission of Form 8038-B in an electronic format. You would need to register with the IRS and follow their guidelines for using the FIRE system.
Key Takeaways
Form 8038-B is a critical component of the municipal bond issuance process for Build America Bonds and Recovery Zone Economic Development Bonds.
By providing comprehensive information about the bond issuance and its usage, the IRS can ensure compliance with tax laws and monitor the intended economic impact of these bonds.
As an investor or issuer of municipal bonds, understanding the significance of Form 8038-B and adhering to its requirements is essential. It not only ensures smooth transactions but also contributes to the overall success of infrastructure development and economic growth in communities across the United States.


