- IRS forms
- Form 943
Form 943: A Guide for Agricultural Employers to File Federal Taxes
Download Form 943Introduction
As a small business owner or professional in the United States, you may be required to file Form 943, Employer's Annual Federal Tax Return for Agricultural Employees. This form is used to report wages paid to agricultural workers and to calculate and pay federal taxes on those wages. In this blog post, we will discuss what Form 943 is, who needs to file it, how to file it, when to file it, common mistakes to avoid when filing, and what to do if you encounter an issue.
What is Form 943?
Form 943 is a tax form used by employers to report wages paid to agricultural workers during the year. Agricultural workers are employees who work on a farm, ranch, or other agricultural operation. Employers use this form to calculate and pay their share of Social Security and Medicare taxes, as well as federal income tax withheld from their employee's wages.
Who needs to file Form 943?
Form 943 is used by agricultural employers in the United States to report and pay federal taxes on wages paid to their employees who work on farms, ranches, or other agricultural businesses. An agricultural employer is defined as any individual or organization that hires farm workers, including farmers, ranchers, and agricultural cooperatives.
To determine if you need to file Form 943, there are two tests:
- If you pay cash wages of $150 or more to a farmworker during the calendar year.
- If the total cash and non-cash wages paid to all farmworkers in the previous calendar year are at least $2,500.
If either of these tests is met, Form 943 must be filed. The due date for filing and paying taxes is generally January 31st of the year following the tax year.
How to file Form 943
**Step 1: **Obtain Form 943
The first step is to obtain Form 943. You can download a copy of the form from the IRS website or order a paper copy by calling the IRS at 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676). Once you have the form, review the instructions carefully to ensure that you have all the information you need to complete it.
Step 2: Fill Out the Form
The next step is to fill out the form. The form requires information such as the employer's name and address, EIN, total wages paid to agricultural workers, federal income tax withheld, Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld, and any other taxes owed.
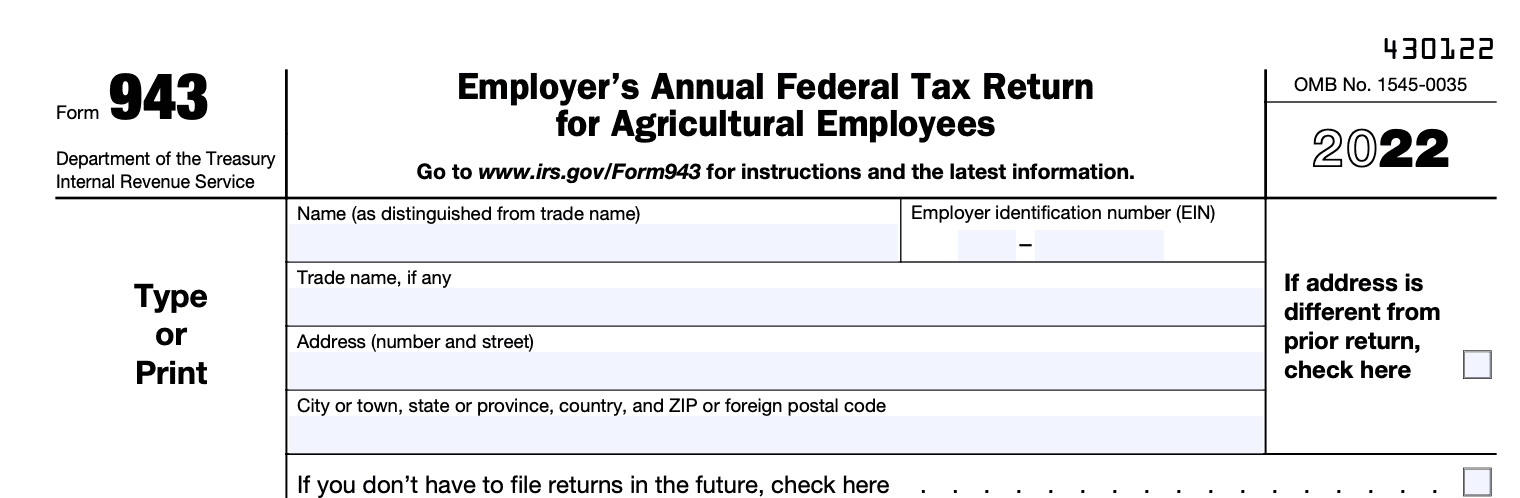
As you can see, the form asks for basic information such as the employer's name and address, as well as the employer identification number (EIN). Be sure to double-check that all information is accurate and up-to-date.
Next, you'll need to report the total wages paid to agricultural workers during the year. This includes any bonuses, vacation pay, or other forms of compensation.
In this section, you'll need to report the total wages paid to agricultural workers, as well as any federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes withheld. Be sure to enter the correct amounts for each employee.
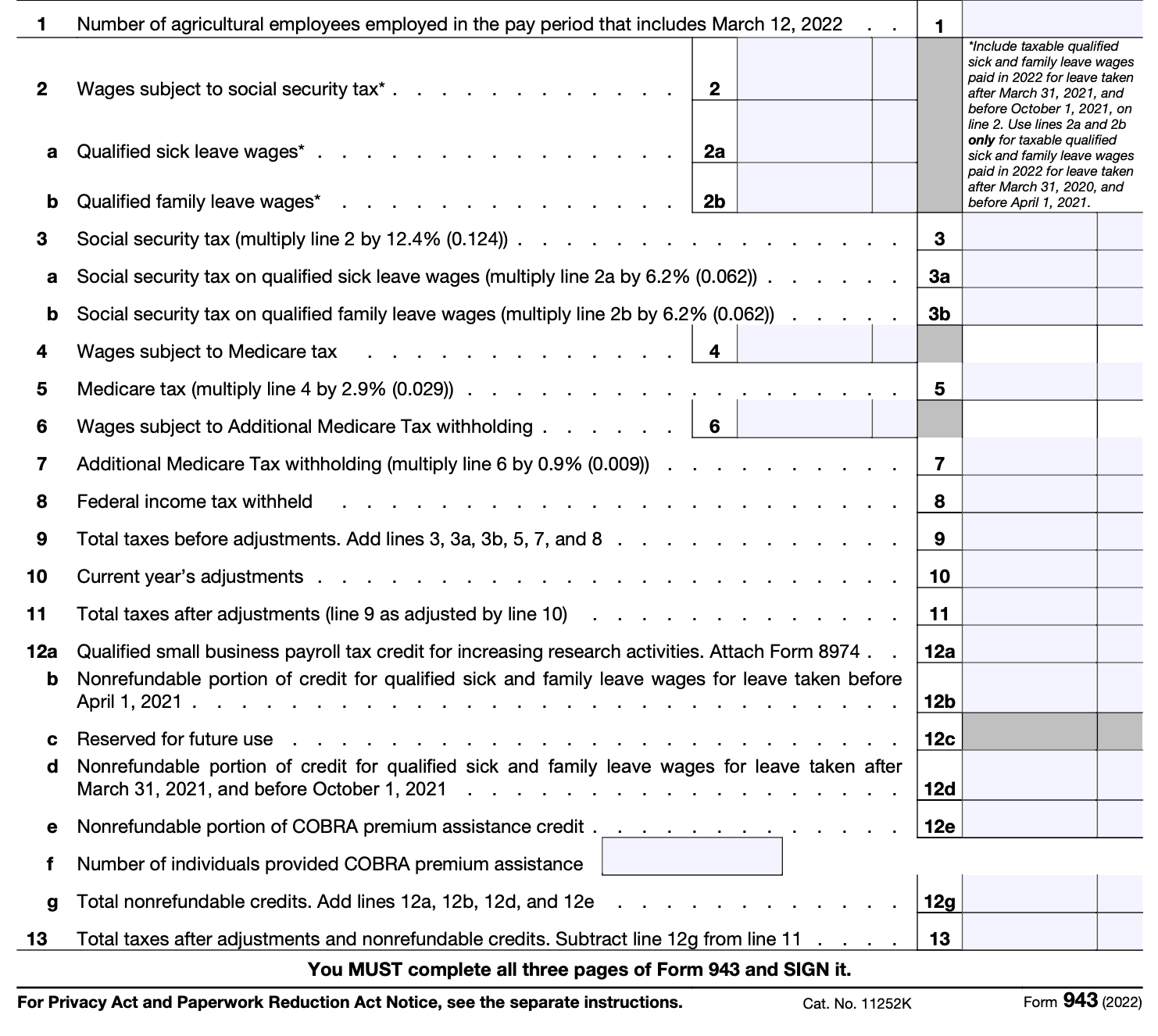
Step 3: Submit the Form and Any Required Payments
Once you've completed the form, you'll need to submit it to the IRS along with any required payments. You can file the form electronically or by mail. If you choose to file electronically, you can use the IRS e-file system or a third-party provider.
If you file by mail, be sure to include any payments due with the form. You can pay by check or money order, or you can use the Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS).
In this section, you'll need to enter the total amount of tax due, as well as any payments or credits. Be sure to double-check that all information is accurate and that you have included any required payments.

Instructions for filing form 943
Line 1: Enter the total number of agricultural employees paid during the pay period that includes March 12, 2022.
Line 2: Enter the total cash wages subject to Social Security Tax.

Line 3: Calculate Social Security Tax due by multiplying the total on line 2 x 12.4%.

Line 4: Enter the total cash wages subject to Medicare Tax paid to employees for farm work during the calendar year.
Line 5: Multiply the total on Line 4 x 2.9% to obtain the total Medicare Tax due.
Line 6: Enter the total wages subject to Additional Medicare Tax for any employee paid over $200,000 in wages for the calendar year.
Line 7: Calculate the Additional Medicare Tax by multiplying line 6 x 0.9%.
Line 8: Enter the amount of federal income tax withheld from cash wages paid to employees.
Line 9: Enter your total taxes before adjustments by adding lines 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8.
Line 10: Enter any tax adjustments, including rounding fractions of cents, adjustments for sick pay, and uncollected employee share of Social Security and Medicare taxes on third-party sick pay or group-term life insurance premiums.
Line 11: Enter total taxes after adjustments.
Line 12: If your business qualifies for a tax credit, enter the amount and fill out Form 8974 and attach it to the completed Form 943.
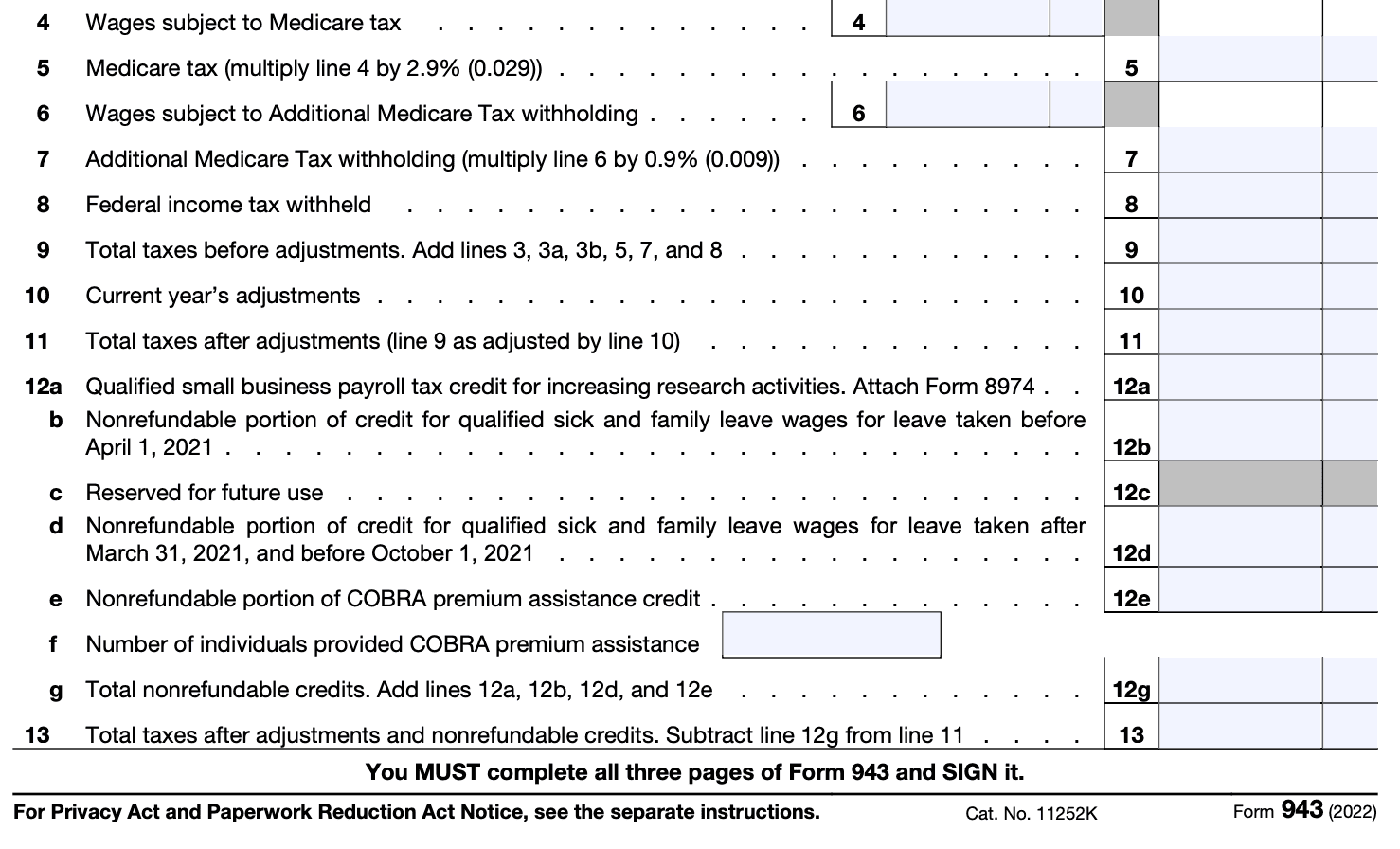
Line 13: Enter your total taxes after any adjustments or credits by subtracting line 12 from line 11.
Line 14: Enter any deposits made during the calendar year, including any overpayments made.

Lines 15-16: Enter your balance due or overpayment, and check if you want the overpayment applied to the next return, or if you wish to have a refund sent to you.

Lines 17-27: Complete these lines only if required, to calculate certain credits (if you decide to claim any).
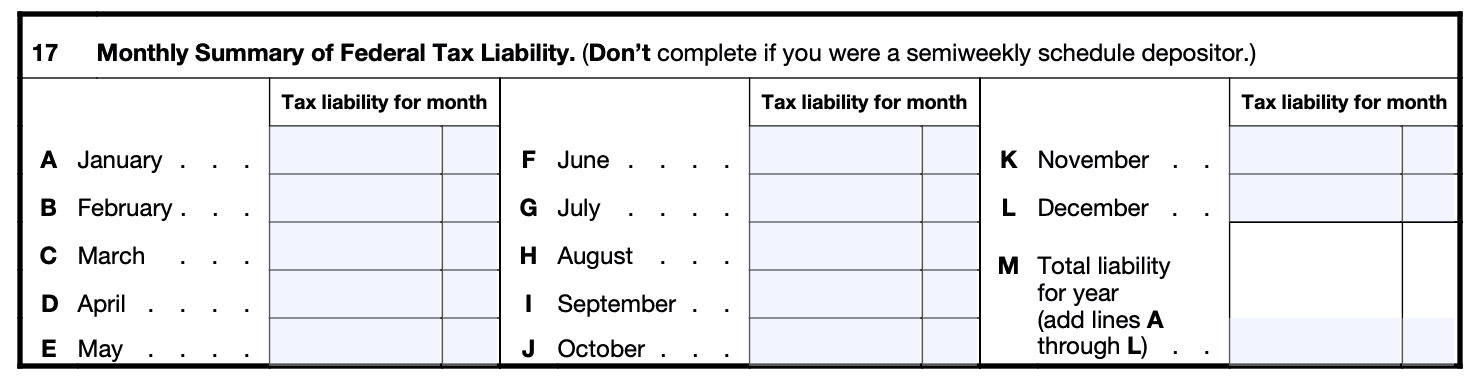
If using payroll software or services, the information needed should be easily accessible from your payroll journal. For additional more detailed instructions for Form 943, please visit IRS.gov.

When to file Form 943?
Form 943 must be filed annually by January 31, or by February 10 if taxes have been deposited throughout the tax year. Make sure to reconcile Form 943 with totals filed on Form W-2 and W-3. You must continue filing Form 943 every year unless your business closes. If your tax liability is less than $2,500 for the entire calendar year, you can pay the tax owed when you file the form. If you use payroll software or a payroll service, Form 943 should be automatically completed for you, but it's your responsibility to ensure it's filed accurately and timely. Consider using specialized payroll software for agribusinesses.
Where to mail Form 943?
Form 943 is not typically filed by email. Instead, it must be submitted to the IRS via mail. The mailing address will vary based on the location of your business. You can find the appropriate mailing address for your location by consulting the instructions for Form 943, which are available on the IRS website. Alternatively, you can contact the IRS directly to confirm the correct mailing address for your specific situation.
It's important to note that you should not send Form 943 to the same address where you send your employment tax deposits. This is because the addresses for filing returns and making payments can be different.
If you prefer to file electronically, you can do so using the IRS's e-file system. However, there are certain requirements that must be met in order to use this option, and not all businesses may qualify. Be sure to check the IRS website or speak with a tax professional to determine whether e-filing is an option for you.
Paper filing vs e-filing of Form 943
Form 943 can be filed either on paper or electronically, depending on your preference and circumstances. Here's a detailed comparison of paper filing and e-filing:
Paper Filing:
- You can obtain Form 943 from the IRS website or by calling the IRS at 1-800-TAX-FORM (1-800-829-3676).
- Once you have filled out the form, you must mail it to the IRS at the address listed on the form, along with any payment due.
- Paper filing requires more time and effort to complete than e-filing, as you need to fill out the form by hand or use a typewriter. Additionally, you need to manually calculate the tax due and check for errors, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- The IRS recommends that you use certified mail or a reputable delivery service when mailing your tax return to ensure that it is received on time.
E-filing:
- You can e-file Form 943 using the IRS's free e-file system or through a tax professional or payroll service provider who offers e-filing services.
- E-filing is a faster and more efficient way of filing Form 943, as you can complete the form online using tax software or a service provider's website. This eliminates the need to manually calculate the tax due, which reduces the likelihood of errors.
- E-filing also provides you with instant confirmation that your tax return has been received by the IRS, which eliminates the risk of lost or delayed mail.
- If you e-file, you may be able to pay any taxes due electronically as well.
- E-filing may be required if you have a certain number of employees or pay a certain amount of wages, so check with the IRS to see if you meet their e-filing requirements.
Both paper filing and e-filing have their pros and cons, so it's up to you to decide which method is best for your business. However, e-filing is generally faster, more accurate, and more convenient than paper filing.
Form 943 Penalties
To avoid penalties and interest charges, make sure to deposit or pay taxes on time, file a completed Form 943 on time, report tax liability accurately, submit valid tax payments, provide employees with accurate Forms W-2, and file Form W-3 and Copy A of Forms W-2 with the SSA on time.
Penalties and interest are charged on late taxes and returns at a legally set rate, details of which can be found in sections 7 and 8 of Pub. 51. To request penalty or interest abatement, use Form 843 and not Form 943 or Form 943-X.
Common mistakes to avoid when filing Form 943
Some common mistakes to avoid when filing Form 943 include:
- Failing to accurately report the total wages paid to agricultural workers
- Failing to withhold and report the correct amount of federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes
- Failing to file the form by the deadline
What to do if you encounter an issue?
If you encounter an issue when filing Form 943, the first step is to contact the IRS for assistance. The IRS provides a number of resources for employers, including phone support and online help. If you receive a notice from the IRS regarding your Form 943, it is important to respond promptly and provide any requested information.
Conclusion
Filing Form 943 is an important responsibility for employers who pay wages to agricultural workers. By understanding the requirements for filing Form 943 and following the correct steps, employers can avoid common mistakes and ensure that they are in compliance with federal tax regulations. If you have any questions about filing Form 943, be sure to contact the IRS or a tax professional for assistance.


